On May 19, 2025, NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang took the stage at the Taipei Music Center to open COMPUTEX 2025, delivering a powerful keynote address to an audience of more than 4,000. His message was clear: the world is entering a new era of transformation. An AI-driven revolution that is poised to reshape every industry, country and company.
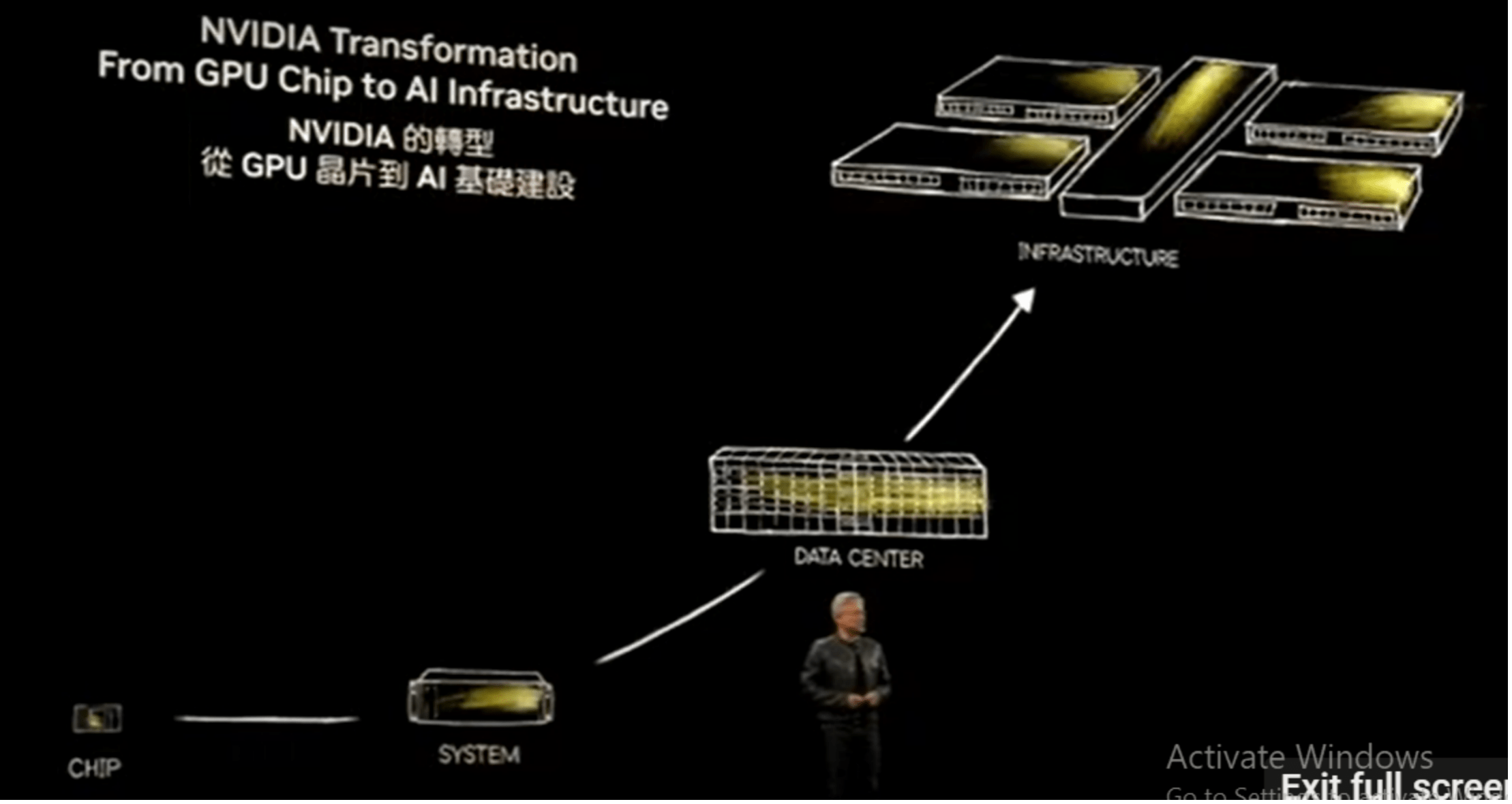
Huang began by tracing past technological revolutions from electricity to the PC, the internet and big data. And he declared that AI is the next foundational technology. “AI is now infrastructure,” he said. “And just like electricity and the internet, AI needs factories.”
“These AI factories are not traditional data centers, according to Huang. They consume vast amounts of energy and vast datasets to produce something very valuable: tokens. These tokens are the building blocks of intelligence that drive content generation, scientific discovery and digital reasoning.” “Tokens open up new frontiers,” he explained. “They can turn images into scientific data and decipher the laws of physics. Intelligence is being produced in this AI factory.”
“Tokens open up new frontiers,” he explained. “They can turn images into scientific data and decipher the laws of physics. Intelligence is being produced in this AI factory.”
“Jensen Huang expressed deep appreciation for Taiwan, a place NVIDIA has been visiting for 30 years. He called Taiwan the heart of the computing ecosystem and emphasized the island’s critical role in launching new products, creating new markets, and building strategic partnerships. If new markets are to be created, they must start in Taiwan.”
He then outlined NVIDIA’s innovations and new direction. One of its key pillars is CUDA-X, a suite of libraries and tools that make AI development easier and more powerful. NVIDIA’s commitment to these libraries is what sets it apart, with CUDA being the foundation of performance in everything from gaming to scientific computing.
Jensen Huang explains how GeForce introduced CUDA to a global audience, enabling real-time rendering through AI-based neural rendering technology. This approach only calculates 1 in 10 pixels, while the rest is predicted by AI to produce stunning visual quality with incredible efficiency.
Celebrating 30 years of PC gaming, Huang introduced the GeForce RTX 50 series. His strategy remains clear: expand CUDA’s reach globally so developers can create transformative applications more easily. A growing developer base and libraries lead to better software, which ultimately benefits users.
NVIDIA’s ecosystem now includes partnerships with SoftBank, T-Mobile, Indosat, Vodafone, Nokia, Samsung, Fujitsu and Cisco. These companies are helping test and deploy AI over 5G and 6G networks, combining AI with next-generation telecommunications.
Quantum computing is also part of Huang’s vision. He introduced CudaQ, a hybrid platform between Quantum and classical. The GPU is used for pre-processing, post-processing and error correction. In the future, Jensen Huang predicts that supercomputers will combine CPUs, GPUs and Quantum Processing Units (QPUs) working simultaneously.
Then explain the evolution of AI:
- Perception AI: recognize patterns, sounds, and visuals
- Generative AI: create content from text, images, and videos; enable universal translation
- Reasoning AI: solve new problems, apply logic, and simulate decisions
- Agentic AI: goal-oriented systems that can plan, reason, and act autonomously; essentially, digital robots
- Physical AI: AI that understands the laws of physics such as inertia, friction, and the existence of objects, allowing robots to operate in the real world
25 years ago we started with perception AI, an AI model that could understand patterns, recognize sounds and images. That was the beginning, and in the last 5 years we have been talking about Generative AI (GenAI), AI that not only understands, but can also generate. It can be from text to text like ChatGPT, from text to image to video, even vice versa. Almost everything to everything. We find universal functions in AI like Universal Translator that can translate from anything to anything. You just tokenize information to understand it.
Now we’ve reached a very important level of AI. GenAI gives us one-shot AI: you give it text and it will give you a response. That was a huge breakthrough that happened two years ago when we first met ChatGPT.
But intelligence isn’t just about learning from data. It also includes the ability to reason.
The ability to solve problems that have never been seen before.
Analyze step by step. Apply rules and theorems to solve new problems. Simulate different possibilities and scenarios.
Technologies like “chain of thought”, “tree of thought”, etc. allow AI to reason effectively.
And now, AI can not only reason, but also understand. When combined with multimodal capabilities, you get Agentic AI.
Agentic AI is able to take a goal, break it down into steps, plan the best way to achieve it, consider the consequences, and then start executing the plan. This process can involve using tools or working with other AI agents.
Agentic AI is basically AI that can think and act like a robot in digital form. This is going to be a big thing in the next few years and we are already seeing great progress in this area.
The next wave after that is Physical AI.
Physical AI
AI that understands the physical world. It understands concepts like inertia, friction, and the existence of objects. For example, if you throw a ball and it rolls under a car, the AI will infer that it is likely to emerge on the other side, rather than just disappear.
If there is a table in front of you, the AI should understand that the best way to get to the other side is to go around it or walk under it, rather than crash into it. The ability to reason about physical things is critical to the next era of AI. Physical AI enables autonomous cars to be trained in real-world scenarios, such as the presence of dogs, birds, or people.
And when these reasoning, generative, and physical abilities are combined, they can be put into a physical form: robots. Imagine if you could tell an AI to make a video about picking up bottles then you could also imagine a real robot doing it. AI is capable of doing that now. And that is the future we are building.
A revolutionary computer called Hopper was introduced three years ago, revolutionizing AI as we know it today. It is one of the most popular and well-known computers in the world. In the last few years, we have developed new computers to enable AI to think very fast—because thinking means generating lots of tokens and processing them over and over again. So, from one-off AI, we are now entering the era of thinking AI, reasoning AI, inference timescale AI, all of which require much more computation.